Blogs
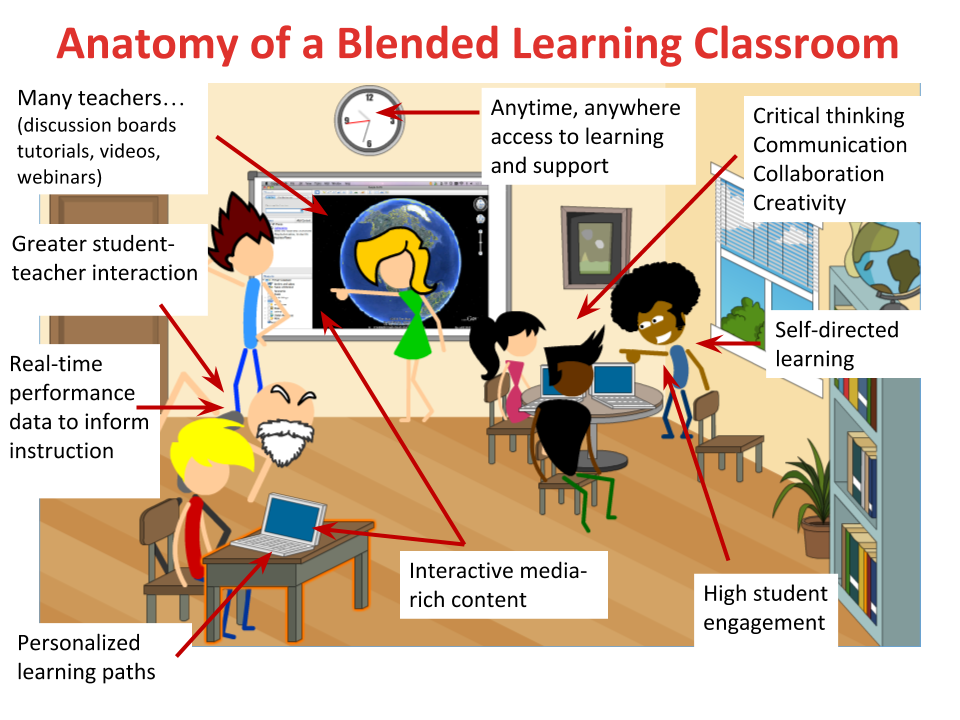
21st Century Classroom
21st Century Classroom
The term "21st-century skills" is generally used to refer to certain core competencies such as collaboration, digital literacy, critical thinking, and problem-solving that advocates believe schools need to teach to help students thrive in today's world.
In the 21st Century classroom, teachers are facilitators of student learning. Lectures on a single subject at a time were the norm in the past and today collaboration is the thread for all student learning.
The 21st Century classroom is student centered, not teacher centered. Teachers no longer function as lecturers but as facilitators of learning. The students are learning by doing, and the teacher acts as a coach, helping students as they work on projects. Students learn to use the inquiry method, and to collaborate with others.
The focus of student learning in this classroom is different. The focus is no longer on learning by memorizing and recalling information but on learning how to learn. Now, students use the information they have learned and demonstrate their mastery of the content in the projects they work on. Students learn how to ask the right questions, how to conduct an appropriate investigation, how to find answers, and how to use information. The emphasis in this classroom is on creating lifelong learners. With this goal in mind, students move beyond the student role to learn through real world experiences.
Just as the classroom is changing, so must the teacher adapt their roles and responsibilities. Teachers are no longer teaching in isolation. They now co-teach, team teach, and collaborate with other department members. Teachers are not the only ones responsible for student learning. Other stakeholders including administrators, board members, parents, and students all share responsibility with the teacher for educating the student.
Traits of 21st century Students
-
Critical thinking, problem solving, reasoning, analysis, interpretation, synthesizing information
-
Research skills and practices, interrogative questioning
-
Creativity, artistry, curiosity, imagination, innovation, personal expression
-
Perseverance, self-direction, planning, self-discipline, adaptability, initiative
-
Oral and written communication, public speaking and presenting, listening
-
Leadership, teamwork, collaboration, cooperation, facility in using virtual workspaces
-
Information and communication technology (ICT) literacy, media and internet literacy, data interpretation and analysis, computer programming
-
Civic, ethical, and social-justice literacy
-
Economic and financial literacy, entrepreneur
-
Global awareness, multicultural literacy, humanitarianism
-
Scientific literacy and reasoning, the scientific method
-
Environmental and conservation literacy, ecosystems understanding
-
Health and wellness literacy, including nutrition, diet, exercise, and public health and safety
1. Let Your Students Lead The Learning
Learning takes place best in environments where students feel empowered to learn. Effective teachers are more like moderators, offering inspiration and guiding students to discover for themselves. Give students the opportunity to be self-learners, which guarantees lifelong learning. This brings us directly to the second point.
2. Create an Inquiry-Based Classroom Environment
If students are to lead the way to learning, they need to be able to ask questions – and then find the means to answer them. Students (and teachers) need to “wonder out loud” as they encounter new information. A KWL chart (What do you Know? What do you Want to know? What have you Learned?) can guide students toward true self-motivated learning.
3. Encourage Collaboration
“We are greater than the sum of our parts.” Herein is the heart of collaboration. A healthy, active classroom is a sharing classroom. Students are social beings, and even more so in a language class. Find every opportunity to allow students to form pairs and small groups. Not only does this encourage the development of speaking and listening skills, but it also teaches students how to effectively achieve goals together.
4. Develop Critical Thinking Skills
Learning is more than memorizing and remembering. Critical thinking skills take students well beyond simple comprehension of information. Students use these skills to solve problems in new situations, make inferences and generalizations, combine information in new patterns, and make judgments based on evidence and criteria. Introduce activities in your lessons that build critical thinking skills along with language skills.
5. Encourage Creativity
Encourage your students to be creative throughout each lesson. Creative activities allow students to express what they’ve learned in a new way. This synthesizing and personalizing of knowledge consolidates learning, and creates an experience that remains with students long after the class is over.
By keeping these strategies in mind as you plan each lesson, you will be encouraging the development of 21st Century skills. Of course, your students may also need time to adjust to this new way of learning. However, they will soon begin to feel empowered to think more critically, to ask questions and seek answers, and to express themselves creatively. Most importantly, their communication skills will become much stronger as a result, which always remains our main objective!
“The illiterate of the 21st century will not be those who cannot read and write, but those who cannot learn, unlearn and relearn.” - Alwin Toffer
Source :
https://oupeltglobalblog.com/2013/10/09/5-ways-to-prepare-your-students-for-the-21st-century/
https://www.edglossary.org/21st-century-skills/
https://www.teacherswithapps.com/the-goal-of-education-in-the-21st-century/
Innovation